
webpack是目前最為流行的打包工具之一,其配置簡單,功能強大,擁有豐富的加載器和插件系統,為前端開發者提供了諸多便利。筆者默認各位看官在閱讀本章之前已經有了一定的使用經驗,所以對webpack的使用方式不做贅述。
閱讀本章,你可以了解到如下內容:
- Webpack打包后代碼結構
- Webpack核心架構 —— Tapable
- Webpack事件流
- Webpack插件實現機制
- Webpack加載器實現機制
Webpack打包后代碼結構
簡單打包
我們首先寫一個最簡單的方法,然后使用webpack進行打包:
// /webpack/bundles/simple/moduleA.js window.printA = function printA() { console.log(`This is module A!`); }
一個比較基本的webpack配置文件:
// /webpack/bundles/simple/webpack.config.js const path = require('path'); const webpack = require('webpack'); const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin'); module.exports = { entry: { main: './moduleA.js' }, output: { path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'), filename: 'simple.bundle.js' }, plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: './index.html' }) ] }
創建一個HTML文件用于在瀏覽器環境下測試:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Webpack - Simple Bundle</title> </head> <body> </body> </html>
執行打包命令webpack 后我們獲得了一個 dist 目錄,我們打開 simple.bundle.js 文件:
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap /******/ // The module cache /******/ var installedModules = {}; /******/ /******/ // The require function /******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { /******/ /******/ // Check if module is in cache /******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) { /******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports; /******/ } /******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) /******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { /******/ i: moduleId, /******/ l: false, /******/ exports: {} /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Execute the module function /******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); /******/ /******/ // Flag the module as loaded /******/ module.l = true; /******/ /******/ // Return the exports of the module /******/ return module.exports; /******/ } /******/ /******/ /******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__) /******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules; /******/ /******/ // expose the module cache /******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules; /******/ /******/ // define getter function for harmony exports /******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) { /******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) { /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { /******/ configurable: false, /******/ enumerable: true, /******/ get: getter /******/ }); /******/ } /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules /******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) { /******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ? /******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } : /******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; }; /******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter); /******/ return getter; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call /******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); }; /******/ /******/ // __webpack_public_path__ /******/ __webpack_require__.p = ""; /******/ /******/ // Load entry module and return exports /******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0); /******/ }) /************************************************************************/ /******/ ([ /* 0 */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { window.printA = function printA() { console.log(`This is module A!`); } /***/ }) /******/ ]);
主要看這段:
// ...... var installedModules = {}; /******/ /******/ // The require function /******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { /******/ /******/ // Check if module is in cache /******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) { /******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports; /******/ } /******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) /******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { /******/ i: moduleId, /******/ l: false, /******/ exports: {} /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Execute the module function /******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); /******/ /******/ // Flag the module as loaded /******/ module.l = true; /******/ /******/ // Return the exports of the module /******/ return module.exports; /******/ } /******/ /******/ /******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__) /******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules; /******/ /******/ // expose the module cache /******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules; /******/ /******/ // define getter function for harmony exports /******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) { /******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) { /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { /******/ configurable: false, /******/ enumerable: true, /******/ get: getter /******/ }); /******/ } /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules /******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) { /******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ? /******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } : /******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; }; /******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter); /******/ return getter; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call /******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); }; /******/ /******/ // __webpack_public_path__ /******/ __webpack_require__.p = ""; /******/ /******/ // Load entry module and return exports /******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0); // ......
webpack內部定義了一個 webpack_require 的方法,這個方法的實質很簡單:
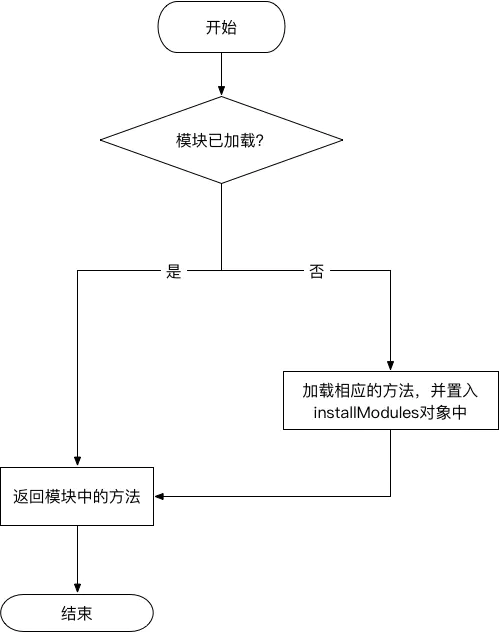
多模塊間存在簡單依賴
例如 moduleB.js 依賴于 moduleA.js 文件。
// /webpack/bundles/simpleDependencies/moduleA.js module.exports = window.printA = function printA() { console.log(`This is module A!`); }
// /webpack/bundles/simpleDependencies/moduleB.js const printA = require('./moduleA'); module.exports = window.printB = function printB() { printA(); console.log('This is module B!'); }
將配置文件中的入口更改為
// /webpack/bundles/simpleDependencies/webpack.config.js // ... main: './moduleB.js' // ...
再次打包,我們獲得如下代碼:
// /webpack/bundles/simpleDependencies/dist/bundle.js /******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap /******/ // The module cache /******/ var installedModules = {}; /******/ /******/ // The require function /******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { /******/ /******/ // Check if module is in cache /******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) { /******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports; /******/ } /******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) /******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { /******/ i: moduleId, /******/ l: false, /******/ exports: {} /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Execute the module function /******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); /******/ /******/ // Flag the module as loaded /******/ module.l = true; /******/ /******/ // Return the exports of the module /******/ return module.exports; /******/ } /******/ /******/ /******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__) /******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules; /******/ /******/ // expose the module cache /******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules; /******/ /******/ // define getter function for harmony exports /******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) { /******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) { /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { /******/ configurable: false, /******/ enumerable: true, /******/ get: getter /******/ }); /******/ } /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules /******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) { /******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ? /******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } : /******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; }; /******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter); /******/ return getter; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call /******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); }; /******/ /******/ // __webpack_public_path__ /******/ __webpack_require__.p = ""; /******/ /******/ // Load entry module and return exports /******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0); /******/ }) /************************************************************************/ /******/ ([ /* 0 */ /***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) { const printA = __webpack_require__(1); module.exports = window.printB = function printB() { printA(); console.log('This is module B!'); } /***/ }), /* 1 */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { module.exports = window.printA = function printA() { console.log(`This is module A!`); } /***/ }) /******/ ]);
我們可以發現這塊有點變化:
/* 0 */ /***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) { const printA = __webpack_require__(1); module.exports = window.printB = function printB() { printA(); console.log('This is module B!'); }
在 moduleB.js 中,需要依賴 moduleA ,因而需要先執行 __webpack_require(1) 拿到模塊A后,再進行下一步。
多入口
需要注意,打包的文件中moudleId是不會重復的,如果有兩個入口文件的情況,則入口模塊id都為0,其他依賴模塊id不重復。我們創建如下幾個文件,其中 index0.js 依賴于 common.js 與 dependency.js ,而 index1.js 依賴于 index0.js 和 common.js 兩個文件。
// /webpack/bundles/multi/common.js module.exports = function() { console.log('This is common module!'); }
// /webpack/bundles/multi/dependency .js module.exports = function() { console.log('This is dependency module!'); }
// /webpack/bundles/multi/index0.js const common = require('./common'); const dependency = require('./dependency'); module.exports = window.print0 = function() { common(); dependency(); console.log('This is module 0!'); }
// /webpack/bundles/multi/index1.js const common = require('./common'); const index0 = require('./index0'); module.exports = window.print1 = function() { common(); console.log('This is module 1!'); }
修改 webpack.config.js 中的文件入口:
// /webpack/bundles/multi/webpack.config.js // ... entry: { index0: './index0.js', index1: './index1.js' }, output: { path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'), filename: '[name].bundle.js' }, // ...
打包后的文件:
// /webpack/bundles/multi/dist/index0.bundle.js /******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap /******/ // The module cache /******/ var installedModules = {}; /******/ /******/ // The require function /******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { /******/ /******/ // Check if module is in cache /******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) { /******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports; /******/ } /******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) /******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { /******/ i: moduleId, /******/ l: false, /******/ exports: {} /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Execute the module function /******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); /******/ /******/ // Flag the module as loaded /******/ module.l = true; /******/ /******/ // Return the exports of the module /******/ return module.exports; /******/ } /******/ /******/ /******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__) /******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules; /******/ /******/ // expose the module cache /******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules; /******/ /******/ // define getter function for harmony exports /******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) { /******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) { /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { /******/ configurable: false, /******/ enumerable: true, /******/ get: getter /******/ }); /******/ } /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules /******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) { /******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ? /******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } : /******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; }; /******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter); /******/ return getter; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call /******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); }; /******/ /******/ // __webpack_public_path__ /******/ __webpack_require__.p = ""; /******/ /******/ // Load entry module and return exports /******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 1); /******/ }) /************************************************************************/ /******/ ([ /* 0 */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { module.exports = function() { console.log('This is common module!'); } /***/ }), /* 1 */ /***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) { const common = __webpack_require__(0); const dependency = __webpack_require__(2); module.exports = window.print0 = function() { common(); dependency(); console.log('This is module 0!'); } /***/ }), /* 2 */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { module.exports = function() { console.log('This is dependency module!'); } /***/ }) /******/ ]);
// /webpack/bundles/multi/dist/index1.bundle.js /******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap /******/ // The module cache /******/ var installedModules = {}; /******/ /******/ // The require function /******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { /******/ /******/ // Check if module is in cache /******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) { /******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports; /******/ } /******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) /******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { /******/ i: moduleId, /******/ l: false, /******/ exports: {} /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Execute the module function /******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); /******/ /******/ // Flag the module as loaded /******/ module.l = true; /******/ /******/ // Return the exports of the module /******/ return module.exports; /******/ } /******/ /******/ /******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__) /******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules; /******/ /******/ // expose the module cache /******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules; /******/ /******/ // define getter function for harmony exports /******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) { /******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) { /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { /******/ configurable: false, /******/ enumerable: true, /******/ get: getter /******/ }); /******/ } /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules /******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) { /******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ? /******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } : /******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; }; /******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter); /******/ return getter; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call /******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); }; /******/ /******/ // __webpack_public_path__ /******/ __webpack_require__.p = ""; /******/ /******/ // Load entry module and return exports /******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 3); /******/ }) /************************************************************************/ /******/ ([ /* 0 */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { module.exports = function() { console.log('This is common module!'); } /***/ }), /* 1 */ /***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) { const common = __webpack_require__(0); const dependency = __webpack_require__(2); module.exports = window.print0 = function() { common(); dependency(); console.log('This is module 0!'); } /***/ }), /* 2 */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { module.exports = function() { console.log('This is dependency module!'); } /***/ }), /* 3 */ /***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) { const common = __webpack_require__(0); const index0 = __webpack_require__(1); module.exports = window.print1 = function() { common(); console.log('This is module 1!'); } /***/ }) /******/ ]);
顯然,在未使用 CommonsChunkPlugin 這個插件之前,這兩個文件是存在重復代碼的。也就是每個入口都會獨立進行打包。
我們看如果添加了 CommonsChunkPlugin 這個插件后的情況(修改 webpack.config.js):
// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/webpack.config.js plugins: [ // ... new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ name: 'common', filename: 'common.js' }) ]
這樣一來會生成三個文件,index0.bundle.js ,index1.bundel.js 以及 common.js:
// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/dist/common.js /******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap /******/ // install a JSONP callback for chunk loading /******/ var parentJsonpFunction = window["webpackJsonp"]; /******/ window["webpackJsonp"] = function webpackJsonpCallback(chunkIds, moreModules, executeModules) { /******/ // add "moreModules" to the modules object, /******/ // then flag all "chunkIds" as loaded and fire callback /******/ var moduleId, chunkId, i = 0, resolves = [], result; /******/ for(;i < chunkIds.length; i++) { /******/ chunkId = chunkIds[i]; /******/ if(installedChunks[chunkId]) { /******/ resolves.push(installedChunks[chunkId][0]); /******/ } /******/ installedChunks[chunkId] = 0; /******/ } /******/ for(moduleId in moreModules) { /******/ if(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(moreModules, moduleId)) { /******/ modules[moduleId] = moreModules[moduleId]; /******/ } /******/ } /******/ if(parentJsonpFunction) parentJsonpFunction(chunkIds, moreModules, executeModules); /******/ while(resolves.length) { /******/ resolves.shift()(); /******/ } /******/ if(executeModules) { /******/ for(i=0; i < executeModules.length; i++) { /******/ result = __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = executeModules[i]); /******/ } /******/ } /******/ return result; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // The module cache /******/ var installedModules = {}; /******/ /******/ // objects to store loaded and loading chunks /******/ var installedChunks = { /******/ 2: 0 /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // The require function /******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { /******/ /******/ // Check if module is in cache /******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) { /******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports; /******/ } /******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) /******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { /******/ i: moduleId, /******/ l: false, /******/ exports: {} /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Execute the module function /******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); /******/ /******/ // Flag the module as loaded /******/ module.l = true; /******/ /******/ // Return the exports of the module /******/ return module.exports; /******/ } /******/ /******/ /******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__) /******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules; /******/ /******/ // expose the module cache /******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules; /******/ /******/ // define getter function for harmony exports /******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) { /******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) { /******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { /******/ configurable: false, /******/ enumerable: true, /******/ get: getter /******/ }); /******/ } /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules /******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) { /******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ? /******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } : /******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; }; /******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter); /******/ return getter; /******/ }; /******/ /******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call /******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); }; /******/ /******/ // __webpack_public_path__ /******/ __webpack_require__.p = ""; /******/ /******/ // on error function for async loading /******/ __webpack_require__.oe = function(err) { console.error(err); throw err; }; /******/ }) /************************************************************************/ /******/ ([ /* 0 */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { module.exports = function() { console.log('This is common module!'); } /***/ }), /* 1 */ /***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) { const common = __webpack_require__(0); const dependency = __webpack_require__(2); module.exports = window.print0 = function() { common(); dependency(); console.log('This is module 0!'); } /***/ }), /* 2 */ /***/ (function(module, exports) { module.exports = function() { console.log('This is dependency module!'); } /***/ }) /******/ ]);
common.js 已經包含了所有的公共方法,并且在瀏覽器 window 對象中創建了一個名為 webpackJsonp 的方法。
// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/dist/common.js // ... /******/ var parentJsonpFunction = window["webpackJsonp"]; /******/ window["webpackJsonp"] = function webpackJsonpCallback(chunkIds, moreModules, executeModules) { /******/ // add "moreModules" to the modules object, /******/ // then flag all "chunkIds" as loaded and fire callback /******/ var moduleId, chunkId, i = 0, resolves = [], result; /******/ for(;i < chunkIds.length; i++) { /******/ chunkId = chunkIds[i]; /******/ if(installedChunks[chunkId]) { /******/ resolves.push(installedChunks[chunkId][0]); /******/ } /******/ installedChunks[chunkId] = 0; /******/ } /******/ for(moduleId in moreModules) { /******/ if(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(moreModules, moduleId)) { /******/ modules[moduleId] = moreModules[moduleId]; /******/ } /******/ } /******/ if(parentJsonpFunction) parentJsonpFunction(chunkIds, moreModules, executeModules); /******/ while(resolves.length) { /******/ resolves.shift()(); /******/ } /******/ if(executeModules) { /******/ for(i=0; i < executeModules.length; i++) { /******/ result = __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = executeModules[i]); /******/ } /******/ } /******/ return result; /******/ }; // ... /******/ // objects to store loaded and loading chunks /******/ var installedChunks = { /******/ 2: 0 /******/ }; // ...
這個方法與 __webpack_require__ 較為類似,同樣也是將模塊緩存進來。只不過 webpack 會預先抽取公共模塊,先將其緩存進來,而后可以在其他的 bundle.js 中使用 webpackJsonp 方法進行模塊加載。
// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/dist/index0.bundle.js webpackJsonp([1],[],[1]);
// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/dist/index1.bundle.js webpackJsonp([0],{ /***/ 3: /***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) { const common = __webpack_require__(0); const index0 = __webpack_require__(1); module.exports = window.print1 = function() { common(); console.log('This is module 1!'); } /***/ }) },[3]);
Webpack核心架構 —— Tapable
從github上將webpack源碼克隆至本地,我們可以先了解到 webpack 的一個整體流程:
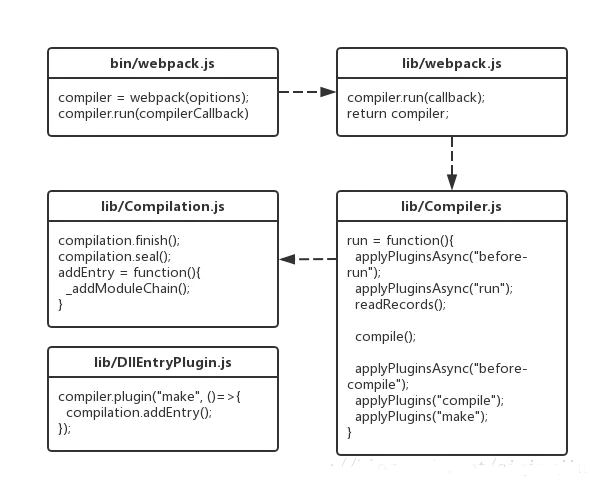
- lib/webpack.js中返回一個compiler對象,并調用了compiler.run()
- lib/Compiler.js中,run方法觸發了before-run、run兩個事件,然后通過readRecords讀取文件,通過compile進行打包,打包后觸發before-compile、compile、make等事件;compile是主要流程,該方法中實例化了一個Compilation類,并調用了其finish及seal方法。
- lib/Compilation.js中定義了finish及seal方法,還有一個重要方法addEntry。這個方法通過調用其私有方法_addModuleChain完成了兩件事:根據模塊的類型獲取對應的模塊工廠并創建模塊;構建模塊。
- lib/Compiler.js中沒有顯式調用addEntry,而是觸發make事件,lib/DllEntryPlugin.js為一個監聽make事件的插件,在回調函數中調用了addEntry。
具體分析_addModuleChain,其完成的第二件事構建模塊又可以分為三部分:
- 調用loader處理模塊之間的依賴。
- 將loader處理后的文件通過acorn抽象成抽象語法樹AST。
- 遍歷AST,構建該模塊的所有依賴。
具體看 lib/webpack.js 這個文件,此文件為 webpack 的入口文件。
const webpack = (options, callback) => { const webpackOptionsValidationErrors = validateSchema( webpackOptionsSchema, options ); if (webpackOptionsValidationErrors.length) { throw new WebpackOptionsValidationError(webpackOptionsValidationErrors); } let compiler; if (Array.isArray(options)) { compiler = new MultiCompiler(options.map(options => webpack(options))); } else if (typeof options === "object") { options = new WebpackOptionsDefaulter().process(options); compiler = new Compiler(options.context); compiler.options = options; new NodeEnvironmentPlugin().apply(compiler); if (options.plugins && Array.isArray(options.plugins)) { for (const plugin of options.plugins) { plugin.apply(compiler); } } compiler.hooks.environment.call(); compiler.hooks.afterEnvironment.call(); compiler.options = new WebpackOptionsApply().process(options, compiler); } else { throw new Error("Invalid argument: options"); } if (callback) { if (typeof callback !== "function") throw new Error("Invalid argument: callback"); if ( options.watch === true || (Array.isArray(options) && options.some(o => o.watch)) ) { const watchOptions = Array.isArray(options) ? options.map(o => o.watchOptions || {}) : options.watchOptions || {}; return compiler.watch(watchOptions, callback); } compiler.run(callback); } return compiler; };
lib/webpack.js 中流程大致如下:
- 參數驗證
- 創建
Compiler(編譯器)對象 - 注冊并執行
NodeEnvironmentPlugin - 執行鉤子
environment里的方法 - 執行鉤子
afterEnvironment里的方法 - 注冊并執行各種插件
- 將
compiler向外導出
顯然,Compiler是我們需要深究的一個部分,因為 webpack 最終向外部返回也就是這個 Compiler 實例。大致了解下 Compiler 的實現:
class Compiler extends Tapable { constructor(context) { super(); this.hooks = { // ... }; this._pluginCompat.tap("Compiler", options => { // ... }); // ... this.resolvers = { normal: { // ... }, loader: { // ... }, context: { // ... } }; // ... } watch(watchOptions, handler) { // ... } run(callback) { // ... } runAsChild(callback) { // ... } purgeInputFileSystem() { // ... } emitAssets(compilation, callback) { // ... } emitRecords(callback) { // ... } readRecords(callback) { // ... } createChildCompiler( compilation, compilerName, compilerIndex, outputOptions, plugins ) { // ... } isChild() { // ... } createCompilation() { // ... } newCompilation(params) { // ... } createNormalModuleFactory() { // ... } createContextModuleFactory() { // ... } newCompilationParams() { // ... } compile(callback) { // ... } }
Compiler 繼承自 Tapable,在其構造方法中,定義了一些事件鉤子(hooks)、一些變量以及一些方法。這些變量以及方法目前看來還是非常抽象的,所以我們有必要去了解下 Tapable 的實現。
Tapable的Github主頁 對 Tapable 的介紹如下:
- The tapable packages exposes many Hook classes, which can be used to create hooks for plugins.
實際上,webpack基于事件流機制,它的工作流程就是將各個插件串聯起來,而實現這一切的核心就是Tapable,webpack中最核心的負責編譯的Compiler和負責創建bundles的Compilation都是Tapable的實例。Tapable 向外暴露許多的鉤子類,這些類可以很方便地為插件創建事件鉤子。 Tapable 中定義了如下幾種鉤子類:
- SyncHook
- SyncBailHook
- SyncWaterfallHook
- SyncLoopHook
- AsyncParallelHook
- AsyncParallelBailHook
- AsyncSeriesHook
- AsyncSeriesBailHook
- AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
所有鉤子類的構造函數都接收一個可選的參數,這個參數是一個由字符串參數組成的數組,如下:
const hook = new SyncHook(["arg1", "arg2", "arg3"]);
鉤子概覽
Tapable的鉤子分為兩類,同步和異步,其中異步又分為并行和串行:
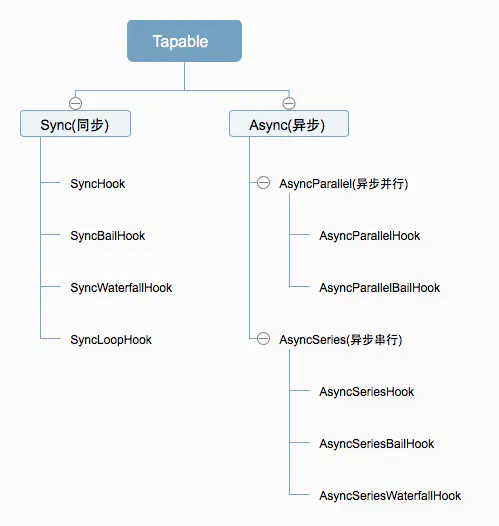
每種鉤子都有各自的使用方式,如下表:
| 序號 | 鉤子名 | 執行方式 | 使用要點 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SyncHook | 同步串行 | 不關心監聽函數的返回值 |
| 2 | SyncBailHook | 同步串行 | 只要監聽函數中有一個函數的返回值不為 null,則跳過剩下所有的邏輯 |
| 3 | SyncWaterfallHook | 同步串行 | 上一個監聽函數的返回值可以傳給下一個監聽函數 |
| 4 | SyncLoopHook | 同步循環 | 當監聽函數被觸發的時候,如果該監聽函數返回true時則這個監聽函數會反復執行,如果返回 undefined 則表示退出循環 |
| 5 | AsyncParallelHook | 異步并發 | 不關心監聽函數的返回值 |
| 6 | AsyncParallelBailHook | 異步并發 | 只要監聽函數的返回值不為 null,就會忽略后面的監聽函數執行,直接跳躍到callAsync等觸發函數綁定的回調函數,然后執行這個被綁定的回調函數 |
| 7 | AsyncSeriesHook | 異步串行 | 不關系callback()的參數 |
| 8 | AsyncSeriesBailHook | 異步串行 | callback()的參數不為null,就會直接執行callAsync等觸發函數綁定的回調函數 |
| 9 | AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook | 異步串行 | 上一個監聽函數的中的callback(err, data)的第二個參數,可以作為下一個監聽函數的參數 |
Sync鉤子
同步串行
(1) SyncHook
不關心監聽函數的返回值
- 使用
const { SyncHook } = require("tapable"); let queue = new SyncHook(['name']); //所有的構造函數都接收一個可選的參數,這個參數是一個字符串的數組。 // 訂閱 queue.tap('1', function (name, name2) {// tap 的第一個參數是用來標識訂閱的函數的 console.log(name, name2, 1); return '1' }); queue.tap('2', function (name) { console.log(name, 2); }); queue.tap('3', function (name) { console.log(name, 3); }); // 發布 queue.call('webpack', 'webpack-cli');// 發布的時候觸發訂閱的函數 同時傳入參數 // 執行結果: /* webpack undefined 1 // 傳入的參數需要和new實例的時候保持一致,否則獲取不到多傳的參數 webpack 2 webpack 3 */
- 原理
class SyncHook_MY{ constructor(){ this.hooks = []; } // 訂閱 tap(name, fn){ this.hooks.push(fn); } // 發布 call(){ this.hooks.forEach(hook => hook(...arguments)); } }
(2) SyncBailHook
只要監聽函數中有一個函數的返回值不為 null,則跳過剩下所有的邏輯
- 使用
const { SyncBailHook } = require("tapable"); let queue = new SyncBailHook(['name']); queue.tap('1', function (name) { console.log(name, 1); }); queue.tap('2', function (name) { console.log(name, 2); return 'wrong' }); queue.tap('3', function (name) { console.log(name, 3); }); queue.call('webpack'); // 執行結果: /* webpack 1 webpack 2 */
- 原理
class SyncBailHook_MY { constructor() { this.hooks = []; } // 訂閱 tap(name, fn) { this.hooks.push(fn); } // 發布 call() { for (let i = 0, l = this.hooks.length; i < l; i++) { let hook = this.hooks[i]; let result = hook(...arguments); if (result) { break; } } } }
(3) SyncWaterfallHook
上一個監聽函數的返回值可以傳給下一個監聽函數
- 使用
const { SyncWaterfallHook } = require("tapable"); let queue = new SyncWaterfallHook(['name']); // 上一個函數的返回值可以傳給下一個函數 queue.tap('1', function (name) { console.log(name, 1); return 1; }); queue.tap('2', function (data) { console.log(data, 2); return 2; }); queue.tap('3', function (data) { console.log(data, 3); }); queue.call('webpack'); // 執行結果: /* webpack 1 1 2 2 3 */
- 原理
class SyncWaterfallHook_MY{ constructor(){ this.hooks = []; } // 訂閱 tap(name, fn){ this.hooks.push(fn); } // 發布 call(){ let result = null; for(let i = 0, l = this.hooks.length; i < l; i++) { let hook = this.hooks[i]; result = i == 0 ? hook(...arguments): hook(result); } } }
(4) SyncLoopHook
當監聽函數被觸發的時候,如果該監聽函數返回true時則這個監聽函數會反復執行,如果返回 undefined 則表示退出循環。
- 使用
const { SyncLoopHook } = require("tapable"); let queue = new SyncLoopHook(['name']); let count = 3; queue.tap('1', function (name) { console.log('count: ', count--); if (count > 0) { return true; } return; }); queue.call('webpack'); // 執行結果: /* count: 3 count: 2 count: 1 */
- 原理
class SyncLoopHook_MY { constructor() { this.hook = null; } // 訂閱 tap(name, fn) { this.hook = fn; } // 發布 call() { let result; do { result = this.hook(...arguments); } while (result) } }
Async鉤子
異步并行
(1) AsyncParallelHook
不關心監聽函數的返回值。有三種注冊/發布的模式,如下:
| 異步訂閱 | 調用方法 |
|---|---|
| tap | callAsync |
| tapAsync | callAsync |
| tapPromise | promise |
- usage – tap
const { AsyncParallelHook } = require("tapable"); let queue1 = new AsyncParallelHook(['name']); console.time('cost'); queue1.tap('1', function (name) { console.log(name, 1); }); queue1.tap('2', function (name) { console.log(name, 2); }); queue1.tap('3', function (name) { console.log(name, 3); }); queue1.callAsync('webpack', err => { console.timeEnd('cost'); }); // 執行結果 /* webpack 1 webpack 2 webpack 3 cost: 4.520ms */
- usage – tapAsync
let queue2 = new AsyncParallelHook(['name']); console.time('cost1'); queue2.tapAsync('1', function (name, cb) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 1); cb(); }, 1000); }); queue2.tapAsync('2', function (name, cb) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 2); cb(); }, 2000); }); queue2.tapAsync('3', function (name, cb) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 3); cb(); }, 3000); }); queue2.callAsync('webpack', () => { console.log('over'); console.timeEnd('cost1'); }); // 執行結果 /* webpack 1 webpack 2 webpack 3 over time: 3004.411ms */
- usage – promise
let queue3 = new AsyncParallelHook(['name']); console.time('cost3'); queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name, cb) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 1); resolve(); }, 1000); }); }); queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name, cb) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 2); resolve(); }, 2000); }); }); queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name, cb) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 3); resolve(); }, 3000); }); }); queue3.promise('webpack') .then(() => { console.log('over'); console.timeEnd('cost3'); }, () => { console.log('error'); console.timeEnd('cost3'); }); /* webpack 1 webpack 2 webpack 3 over cost3: 3007.925ms */
異步串行
(1) AsyncSeriesHook
不關心callback()的參數。
- usage – tap
const { AsyncSeriesHook } = require("tapable"); // tap let queue1 = new AsyncSeriesHook(['name']); console.time('cost1'); queue1.tap('1', function (name) { console.log(1); return "Wrong"; }); queue1.tap('2', function (name) { console.log(2); }); queue1.tap('3', function (name) { console.log(3); }); queue1.callAsync('zfpx', err => { console.log(err); console.timeEnd('cost1'); }); // 執行結果 /* 1 2 3 undefined cost1: 3.933ms */
- usage – tapAsync
let queue2 = new AsyncSeriesHook(['name']); console.time('cost2'); queue2.tapAsync('1', function (name, cb) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 1); cb(); }, 1000); }); queue2.tapAsync('2', function (name, cb) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 2); cb(); }, 2000); }); queue2.tapAsync('3', function (name, cb) { setTimeout(() => { console.log(name, 3); cb(); }, 3000); }); queue2.callAsync('webpack', (err) => { console.log(err); console.log('over'); console.timeEnd('cost2'); }); // 執行結果 /* webpack 1 webpack 2 webpack 3 undefined over cost2: 6019.621ms */
- usage – promise
let queue3 = new AsyncSeriesHook(['name']); console.time('cost3'); queue3.tapPromise('1',function(name){ return new Promise(function(resolve){ setTimeout(function(){ console.log(name, 1); resolve(); },1000) }); }); queue3.tapPromise('2',function(name,callback){ return new Promise(function(resolve){ setTimeout(function(){ console.log(name, 2); resolve(); },2000) }); }); queue3.tapPromise('3',function(name,callback){ return new Promise(function(resolve){ setTimeout(function(){ console.log(name, 3); resolve(); },3000) }); }); queue3.promise('webapck').then(err=>{ console.log(err); console.timeEnd('cost3'); }); // 執行結果 /* webapck 1 webapck 2 webapck 3 undefined cost3: 6021.817ms */
- 原理
class AsyncSeriesHook_MY { constructor() { this.hooks = []; } tapAsync(name, fn) { this.hooks.push(fn); } callAsync() { var slef = this; var args = Array.from(arguments); let done = args.pop(); let idx = 0; function next(err) { // 如果next的參數有值,就直接跳躍到 執行callAsync的回調函數 if (err) return done(err); let fn = slef.hooks[idx++]; fn ? fn(...args, next) : done(); } next(); } }
(2) AsyncSeriesBailHook
callback()的參數不為null,就會直接執行callAsync等觸發函數綁定的回調函數。
- usage – tap
const { AsyncSeriesBailHook } = require("tapable"); // tap let queue1 = new AsyncSeriesBailHook(['name']); console.time('cost1'); queue1.tap('1', function (name) { console.log(1); return "Wrong"; }); queue1.tap('2', function (name) { console.log(2); }); queue1.tap('3', function (name) { console.log(3); }); queue1.callAsync('webpack', err => { console.log(err); console.timeEnd('cost1'); }); // 執行結果: /* 1 null cost1: 3.979ms */
- usage – tapAsync
let queue2 = new AsyncSeriesBailHook(['name']); console.time('cost2'); queue2.tapAsync('1', function (name, callback) { setTimeout(function () { console.log(name, 1); callback(); }, 1000) }); queue2.tapAsync('2', function (name, callback) { setTimeout(function () { console.log(name, 2); callback('wrong'); }, 2000) }); queue2.tapAsync('3', function (name, callback) { setTimeout(function () { console.log(name, 3); callback(); }, 3000) }); queue2.callAsync('webpack', err => { console.log(err); console.log('over'); console.timeEnd('cost2'); }); // 執行結果 /* webpack 1 webpack 2 wrong over cost2: 3014.616ms */
- usage – promise
let queue3 = new AsyncSeriesBailHook(['name']); console.time('cost3'); queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { setTimeout(function () { console.log(name, 1); resolve(); }, 1000) }); }); queue3.tapPromise('2', function (name, callback) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { setTimeout(function () { console.log(name, 2); reject(); }, 2000) }); }); queue3.tapPromise('3', function (name, callback) { return new Promise(function (resolve) { setTimeout(function () { console.log(name, 3); resolve(); }, 3000) }); }); queue3.promise('webpack').then(err => { console.log(err); console.log('over'); console.timeEnd('cost3'); }, err => { console.log(err); console.log('error'); console.timeEnd('cost3'); }); // 執行結果: /* webpack 1 webpack 2 undefined error cost3: 3017.608ms */
(3) AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
上一個監聽函數的中的callback(err, data)的第二個參數,可以作為下一個監聽函數的參數
- usage – tap
const { AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook } = require("tapable"); // tap let queue1 = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['name']); console.time('cost1'); queue1.tap('1', function (name) { console.log(name, 1); return 'lily' }); queue1.tap('2', function (data) { console.log(2, data); return 'Tom'; }); queue1.tap('3', function (data) { console.log(3, data); }); queue1.callAsync('webpack', err => { console.log(err); console.log('over'); console.timeEnd('cost1'); }); // 執行結果: /* webpack 1 2 'lily' 3 'Tom' null over cost1: 5.525ms */
- usage – tapAsync
let queue2 = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['name']); console.time('cost2'); queue2.tapAsync('1', function (name, callback) { setTimeout(function () { console.log('1: ', name); callback(null, 2); }, 1000) }); queue2.tapAsync('2', function (data, callback) { setTimeout(function () { console.log('2: ', data); callback(null, 3); }, 2000) }); queue2.tapAsync('3', function (data, callback) { setTimeout(function () { console.log('3: ', data); callback(null, 3); }, 3000) }); queue2.callAsync('webpack', err => { console.log(err); console.log('over'); console.timeEnd('cost2'); }); // 執行結果: /* 1: webpack 2: 2 3: 3 null over cost2: 6016.889ms */
- usage – promise
let queue3 = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['name']); console.time('cost3'); queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name) { return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { setTimeout(function () { console.log('1:', name); resolve('1'); }, 1000) }); }); queue3.tapPromise('2', function (data, callback) { return new Promise(function (resolve) { setTimeout(function () { console.log('2:', data); resolve('2'); }, 2000) }); }); queue3.tapPromise('3', function (data, callback) { return new Promise(function (resolve) { setTimeout(function () { console.log('3:', data); resolve('over'); }, 3000) }); }); queue3.promise('webpack').then(err => { console.log(err); console.timeEnd('cost3'); }, err => { console.log(err); console.timeEnd('cost3'); }); // 執行結果: /* 1: webpack 2: 1 3: 2 over cost3: 6016.703ms */
- 原理
class AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook_MY { constructor() { this.hooks = []; } tapAsync(name, fn) { this.hooks.push(fn); } callAsync() { let self = this; var args = Array.from(arguments); let done = args.pop(); console.log(args); let idx = 0; let result = null; function next(err, data) { if (idx >= self.hooks.length) return done(); if (err) { return done(err); } let fn = self.hooks[idx++]; if (idx == 1) { fn(...args, next); } else { fn(data, next); } } next(); } }
Tapable事件流
webpack中的事件歸納如下,這些事件出現的順序固定,但不一定每次打包所有事件都觸發:
| 類型 | 名字 | 事件名 |
|---|---|---|
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | entry-option |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-plugins |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-resolvers |
| [A] | applyPlugins | environment |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-environment |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | run |
| [A] | applyPlugins | normal-module-factory |
| [A] | applyPlugins | context-module-factory |
| [A] | applyPlugins | compile |
| [A] | applyPlugins | this-compilation |
| [A] | applyPlugins | compilation |
| [F] | applyPluginsParallel | make |
| [E] | applyPluginsAsyncWaterfall | before-resolve |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | factory |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | resolver |
| [A] | applyPlugins | resolve |
| [A] | applyPlugins | resolve-step |
| [G] | applyPluginsParallelBailResult | file |
| [G] | applyPluginsParallelBailResult | directory |
| [A] | applyPlugins | resolve-step |
| [G] | applyPluginsParallelBailResult | result |
| [E] | applyPluginsAsyncWaterfall | after-resolve |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | create-module |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module |
| [A] | applyPlugins | build-module |
| [A] | applyPlugins | normal-module-loader |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | program |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | statement |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate CallExpression |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | var data |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Identifier |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Identifier require |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | call require |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Literal |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | call require:amd:array |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Literal |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | call require:commonjs:item |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | statement |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate MemberExpression |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Identifier console.log |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | call console.log |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | expression console.log |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | expression console |
| [A] | applyPlugins | succeed-module |
| [E] | applyPluginsAsyncWaterfall | before-resolve |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | factory |
| [A] | applyPlugins | build-module |
| [A] | applyPlugins | succeed-module |
| [A] | applyPlugins | seal |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-modules |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-modules |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-chunks |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-chunks |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | optimize-tree |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-tree |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | should-record |
| [A] | applyPlugins | revive-modules |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-module-order |
| [A] | applyPlugins | before-module-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-module-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-module-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | record-modules |
| [A] | applyPlugins | revive-chunks |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-chunk-order |
| [A] | applyPlugins | before-chunk-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-chunk-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-chunk-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | record-chunks |
| [A] | applyPlugins | before-hash |
| [A] | applyPlugins | hash |
| [A] | applyPlugins | hash-for-chunk |
| [A] | applyPlugins | chunk-hash |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-hash |
| [A] | applyPlugins | before-chunk-assets |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | global-hash-paths |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | global-hash |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | bootstrap |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | local-vars |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | require |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module-obj |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module-require |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | require-extensions |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | asset-path |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | startup |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module-require |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | render |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | render |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | package |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | render |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | package |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | modules |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | render-with-entry |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | asset-path |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | asset-path |
| [A] | applyPlugins | chunk-asset |
| [A] | applyPlugins | additional-chunk-assets |
| [A] | applyPlugins | record |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | additional-assets |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | optimize-chunk-assets |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-chunk-assets |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | optimize-assets |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-assets |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | after-compile |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | should-emit |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | emit |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | asset-path |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | after-emit |
| [A] | applyPlugins | done |
幾個關鍵的事件對應打包的階段:
- entry-option:初始化options
- run:開始編譯
- make:從entry開始遞歸分析依賴并對依賴進行build
- build-moodule:使用loader加載文件并build模塊
- normal-module-loader:對loader加載的文件用acorn編譯,生成抽象語法樹AST
- program:開始對AST進行遍歷,當遇到require時觸發call require事件
- seal:所有依賴build完成,開始對chunk進行優化(抽取公共模塊、加hash等)
- optimize-chunk-assets:壓縮代碼
- emit:把各個chunk輸出到結果文件
了解以上事件,你可以很容易地寫出一個插件。
…未完待續
引用
- Webpack-源碼二,整體調用流程與Tapable事件流
-
webpack4.0源碼分析之Tapable
相關教程推薦:《Web pack入門視頻教程》
 站長資訊網
站長資訊網