
相關(guān)學(xué)習(xí)推薦:java基礎(chǔ)教程
上篇文章我們深入分析了String的內(nèi)存和它的一些特性。本篇文章我們深入的來分析一下與String相關(guān)的另外兩個類,它們分別是StringBuilder和StringBuffer。這兩個類與String有什么關(guān)系呢?首先我們看下下邊這張類圖:
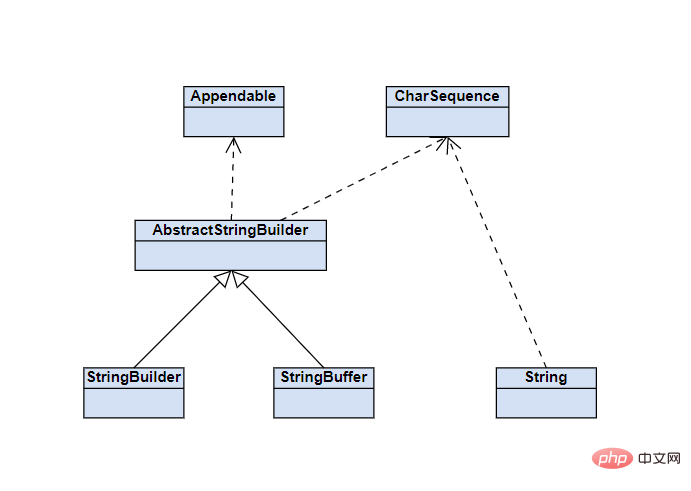
從圖中可以看出StringBuilder和StringBuffer都繼承了AbstractStringBuilder,而AbstractStringBuilder與String實(shí)現(xiàn)了共同的接口CharSequence。
我們知道,字符串是由一系列字符組成的,String的內(nèi)部就是基于char數(shù)組(jdk9之后基于byte數(shù)組)實(shí)現(xiàn)的,而數(shù)組通常是一塊連續(xù)的內(nèi)存區(qū)域,在數(shù)組初始化的時候就需要指定數(shù)組的大小。上一篇文章中我們已經(jīng)知道String是不可變的,因?yàn)樗鼉?nèi)部的數(shù)組被聲明為了final,同時,String的字符拼接、插入、刪除等操作均是通過實(shí)例化新的對象實(shí)現(xiàn)的。而今天要認(rèn)識的StringBuilder和StringBuffer與String相比就具有了動態(tài)性。接下來就讓我們一起來認(rèn)識下這兩個類。
一、StringBuilder
在StringBuilder的父類AbstractStringBuilder 中可以看到如下代碼:
abstract class AbstractStringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence { /** * The value is used for character storage. */ char[] value; /** * The count is the number of characters used. */ int count; }復(fù)制代碼
StringBuilder與String一樣都是基于char數(shù)組實(shí)現(xiàn)的,不同的是StringBuilder沒有final修飾,這就意味著StringBuilder是可以被動態(tài)改變的。接下來看下StringBuilder無參構(gòu)造方法,代碼如下:
/** * Constructs a string builder with no characters in it and an * initial capacity of 16 characters. */ public StringBuilder() { super(16); }復(fù)制代碼
在這個方法中調(diào)用了父類的構(gòu)造方法,到AbstractStringBuilder 中看到其構(gòu)造方法如下:
/** * Creates an AbstractStringBuilder of the specified capacity. */ AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) { value = new char[capacity]; }復(fù)制代碼
AbstractStringBuilder的構(gòu)造方法內(nèi)部初始化了一個容量為capacity的數(shù)組。也就是說StringBuilder默認(rèn)初始化了一個容量為16的char[]數(shù)組。StringBuilder中除了無參構(gòu)造外還提供了多個構(gòu)造方法,源碼如下:
/** * Constructs a string builder with no characters in it and an * initial capacity specified by the {@code capacity} argument. * * @param capacity the initial capacity. * @throws NegativeArraySizeException if the {@code capacity} * argument is less than {@code 0}. */ public StringBuilder(int capacity) { super(capacity); } /** * Constructs a string builder initialized to the contents of the * specified string. The initial capacity of the string builder is * {@code 16} plus the length of the string argument. * * @param str the initial contents of the buffer. */ public StringBuilder(String str) { super(str.length() + 16); append(str); } /** * Constructs a string builder that contains the same characters * as the specified {@code CharSequence}. The initial capacity of * the string builder is {@code 16} plus the length of the * {@code CharSequence} argument. * * @param seq the sequence to copy. */ public StringBuilder(CharSequence seq) { this(seq.length() + 16); append(seq); }復(fù)制代碼
這段代碼的第一個方法初始化一個指定容量大小的StringBuilder。另外兩個構(gòu)造方法分別可以傳入String和CharSequence來初始化StringBuilder,這兩個構(gòu)造方法的容量均會在傳入字符串長度的基礎(chǔ)上在加上16。
1.StringBuilder的append操作與擴(kuò)容
上篇文章已經(jīng)知道通過StringBuilder的append方法可以進(jìn)行高效的字符串拼接,append方法是如何實(shí)現(xiàn)的呢?這里以append(String)為例,可以看到StringBuilder的append調(diào)用了父類的append方法,其實(shí)不止append,StringBuilder類中操作字符串的方法幾乎都是通過父類來實(shí)現(xiàn)的。append方法源碼如下:
// StringBuilder @Override public StringBuilder append(String str) { super.append(str); return this; } // AbstractStringBuilder public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) { if (str == null) return appendNull(); int len = str.length(); ensureCapacityInternal(count + len); str.getChars(0, len, value, count); count += len; return this; }復(fù)制代碼
在append方法的第一行首先進(jìn)行了null檢查,等于null的時候調(diào)用了appendNull方法。其源碼如下:
private AbstractStringBuilder appendNull() { int c = count; ensureCapacityInternal(c + 4); final char[] value = this.value; value[c++] = 'n'; value[c++] = 'u'; value[c++] = 'l'; value[c++] = 'l'; count = c; return this; }復(fù)制代碼
appendNull方法中首先調(diào)用了ensureCapacityInternal來確保字符串?dāng)?shù)組容量充值,關(guān)于ensureCapacityInternal這個方法下邊再詳細(xì)分析。接下來可以看到把"null"的字符添加到了char[]數(shù)組value中。
上文我們提到,StringBuilder內(nèi)部數(shù)組的默認(rèn)容量是16,因此,在進(jìn)行字符串拼接的時候需要先確保char[]數(shù)組有足夠的容量。因此,在appendNull方法以及append方法中都調(diào)用了ensureCapacityInternal方法來檢查char[]數(shù)組是否有足夠的容量,如果容量不足則會對數(shù)組進(jìn)行擴(kuò)容,ensureCapacityInternal源碼如下:
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0) expandCapacity(minimumCapacity); }復(fù)制代碼
這里判讀如果拼接后的字符串長度大于字符串?dāng)?shù)組的長度則會調(diào)用expandCapacity進(jìn)行擴(kuò)容。
void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) { int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2; if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minimumCapacity; if (newCapacity < 0) { if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity); }復(fù)制代碼
expandCapacity的邏輯也很簡單,首先通過原數(shù)組的長度乘2并加2后計算得到擴(kuò)容后的數(shù)組長度。接下來判斷了newCapacity如果小于minimumCapacity,則將minimumCapacity值賦值給了newCapacity。這里因?yàn)檎{(diào)用expandCapacity方法的不止一個地方,所以加這句代碼確保安全。
而接下來的一句代碼就很有趣了,newCapacity 和minimumCapacity 還有可能小于0嗎?當(dāng)minimumCapacity小于0的時候竟然還拋出了一個OutOfMemoryError異常。其實(shí),這里小于0是因?yàn)樵浇缌恕N覀冎涝谟嬎銠C(jī)中存儲的都是二進(jìn)制,乘2相當(dāng)于向左移了一位。以byte為例,一個byte有8bit,在有符號數(shù)中最左邊的一個bit位是符號位,正數(shù)的符號位為0,負(fù)數(shù)為1。那么一個byte可以表示的大小范圍為[-128~127],而如果一個數(shù)字大于127時則會出現(xiàn)越界,即最左邊的符號位會被左邊第二位的1頂替,就出現(xiàn)了負(fù)數(shù)的情況。當(dāng)然,并不是byte而是int,但是原理是一樣的。
另外在這個方法的最后一句通過Arrays.copyOf進(jìn)行了一個數(shù)組拷貝,其實(shí)Arrays.copyOf在上篇文章中就有見到過,在這里不妨來分析一下這個方法,看源碼:
public static char[] copyOf(char[] original, int newLength) { char[] copy = new char[newLength]; System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; }復(fù)制代碼
咦?copyOf方法中竟然也去實(shí)例化了一個對象!!那不會影響性能嗎?莫慌,看一下這里僅僅是實(shí)例化了一個newLength長度的空數(shù)組,對于數(shù)組的初始化其實(shí)僅僅是指針的移動而已,浪費(fèi)的性能可謂微乎其微。接著這里通過System.arraycopy的native方法將原數(shù)組復(fù)制到了新的數(shù)組中。
2.StringBuilder的subString()方法toString()方法
StringBuilder中其實(shí)沒有subString方法,subString的實(shí)現(xiàn)是在StringBuilder的父類AbstractStringBuilder中的。它的代碼非常簡單,源碼如下:
public String substring(int start, int end) { if (start < 0) throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start); if (end > count) throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end); if (start > end) throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end - start); return new String(value, start, end - start); }復(fù)制代碼
在進(jìn)行了合法判斷之后,substring直接實(shí)例化了一個String對象并返回。這里和String的subString實(shí)現(xiàn)其實(shí)并沒有多大差別。 而StringBuilder的toString方法的實(shí)現(xiàn)其實(shí)更簡單,源碼如下:
@Override public String toString() { // Create a copy, don't share the array return new String(value, 0, count); }復(fù)制代碼
這里直接實(shí)例化了一個String對象并將StringBuilder中的value傳入,我們來看下String(value, 0, count)這個構(gòu)造方法:
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) { if (offset < 0) { throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset); } if (count < 0) { throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count); } // Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1. if (offset > value.length - count) { throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count); } this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count); }復(fù)制代碼
可以看到,在String的這個構(gòu)造方法中又通過Arrays.copyOfRange方法進(jìn)行了數(shù)組拷貝,Arrays.copyOfRange的源碼如下:
public static char[] copyOfRange(char[] original, int from, int to) { int newLength = to - from; if (newLength < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to); char[] copy = new char[newLength]; System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length - from, newLength)); return copy; }復(fù)制代碼
Arrays.copyOfRange與Arrays.copyOf類似,內(nèi)部都是重新實(shí)例化了一個char[]數(shù)組,所以String構(gòu)造方法中的this.value與傳入進(jìn)來的value不是同一個對象。意味著StringBuilder在每次調(diào)用toString的時候生成的String對象內(nèi)部的char[]數(shù)組并不是同一個!這里立一個Falg!
3.StringBuilder的其它方法
StringBuilder除了提供了append方法、subString方法以及toString方法外還提供了還提供了插入(insert)、刪除(delete、deleteCharAt)、替換(replace)、查找(indexOf)以及反轉(zhuǎn)(reverse)等一些列的字符串操作的方法。但由于實(shí)現(xiàn)都非常簡單,這里就不再贅述了。
二、StringBuffer
在第一節(jié)已經(jīng)知道,StringBuilder的方法幾乎都是在它的父類AbstractStringBuilder中實(shí)現(xiàn)的。而StringBuffer同樣繼承了AbstractStringBuilder,這就意味著StringBuffer的功能其實(shí)跟StringBuilder并無太大差別。我們通過StringBuffer幾個方法來看
/** * A cache of the last value returned by toString. Cleared * whenever the StringBuffer is modified. */ private transient char[] toStringCache; @Override public synchronized StringBuffer append(String str) { toStringCache = null; super.append(str); return this; } /** * @throws StringIndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} * @since 1.2 */ @Override public synchronized StringBuffer delete(int start, int end) { toStringCache = null; super.delete(start, end); return this; } /** * @throws StringIndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} * @since 1.2 */ @Override public synchronized StringBuffer insert(int index, char[] str, int offset, int len) { toStringCache = null; super.insert(index, str, offset, len); return this; }@Override public synchronized String substring(int start) { return substring(start, count); } // ...復(fù)制代碼
可以看到在StringBuffer的方法上都加上了synchronized關(guān)鍵字,也就是說StringBuffer的所有操作都是線程安全的。所以,在多線程操作字符串的情況下應(yīng)該首選StringBuffer。 另外,我們注意到在StringBuffer的方法中比StringBuilder多了一個toStringCache的成員變量 ,從源碼中看到toStringCache是一個char[]數(shù)組。它的注釋是這樣描述的:
toString返回的最后一個值的緩存,當(dāng)StringBuffer被修改的時候該值都會被清除。
我們再觀察一下StringBuffer中的方法,發(fā)現(xiàn)只要是操作過操作過StringBuffer中char[]數(shù)組的方法,toStringCache都被置空了!而沒有操作過字符數(shù)組的方法則沒有對其做置空操作。另外,注釋中還提到了 toString方法,那我們不妨來看一看StringBuffer中的 toString,源碼如下:
@Override public synchronized String toString() { if (toStringCache == null) { toStringCache = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, 0, count); } return new String(toStringCache, true); }復(fù)制代碼
這個方法中首先判斷當(dāng)toStringCache 為null時會通過 Arrays.copyOfRange方法對其進(jìn)行賦值,Arrays.copyOfRange方法上邊已經(jīng)分析過了,他會重新實(shí)例化一個char[]數(shù)組,并將原數(shù)組賦值到新數(shù)組中。這樣做有什么影響呢?細(xì)細(xì)思考一下不難發(fā)現(xiàn)在不修改StringBuffer的前提下,多次調(diào)用StringBuffer的toString方法,生成的String對象都共用了同一個字符數(shù)組–toStringCache。這里是StringBuffer和StringBuilder的一點(diǎn)區(qū)別。至于StringBuffer中為什么這么做其實(shí)并沒有很明確的原因,可以參考StackOverRun 《Why StringBuffer has a toStringCache while StringBuilder not?》中的一個回答:
1.因?yàn)镾tringBuffer已經(jīng)保證了線程安全,所以更容易實(shí)現(xiàn)緩存(StringBuilder線程不安全的情況下需要不斷同步toStringCache) 2.可能是歷史原因
三、 總結(jié)
本篇文章到此就結(jié)束了。《深入理解Java中的字符串》通過兩篇文章深入的分析了String、StringBuilder與StringBuffer三個字符串相關(guān)類。這塊內(nèi)容其實(shí)非常簡單,只要花一點(diǎn)時間去讀一下源碼就很容易理解。當(dāng)然,如果你沒看過此部分源碼相信這篇文章能夠幫助到你。不管怎樣,相信大家通過閱讀本文還是能有一些收獲。解了這些知識后可以幫助我們在開發(fā)中對字符串的選用做出更好的選擇。同時,這塊內(nèi)容也是面試常客,相信大家讀完本文去應(yīng)對面試官的問題也會綽綽有余。
想了解
 站長資訊網(wǎng)
站長資訊網(wǎng)